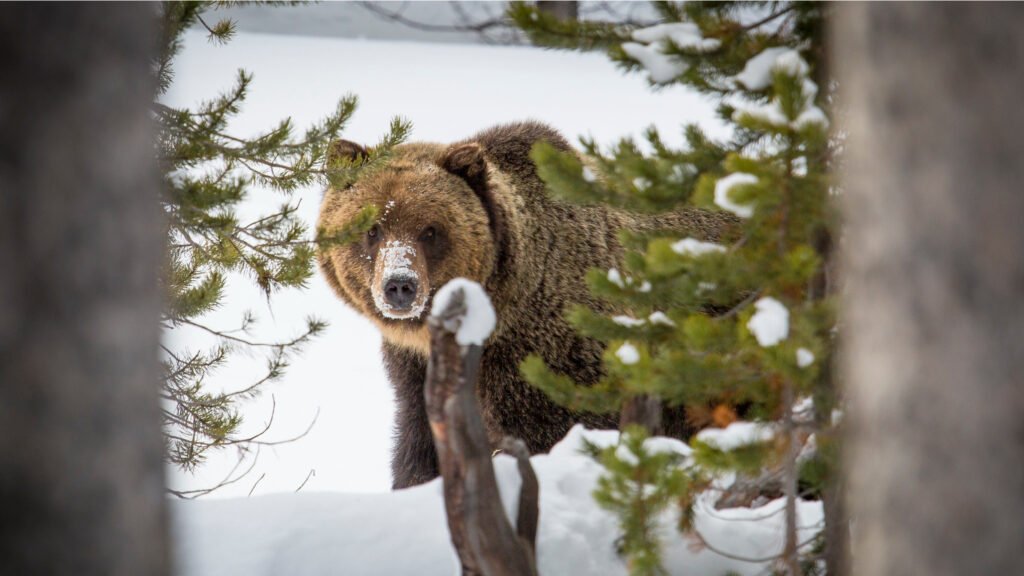
The Bitterroot Mountains of Montana and Idaho are one of many six grizzly bear restoration zones within the Decrease 48, however they nonetheless do not have a breeding inhabitants. USFWS is lastly shifting ahead with decades-old plans to reintroduce them
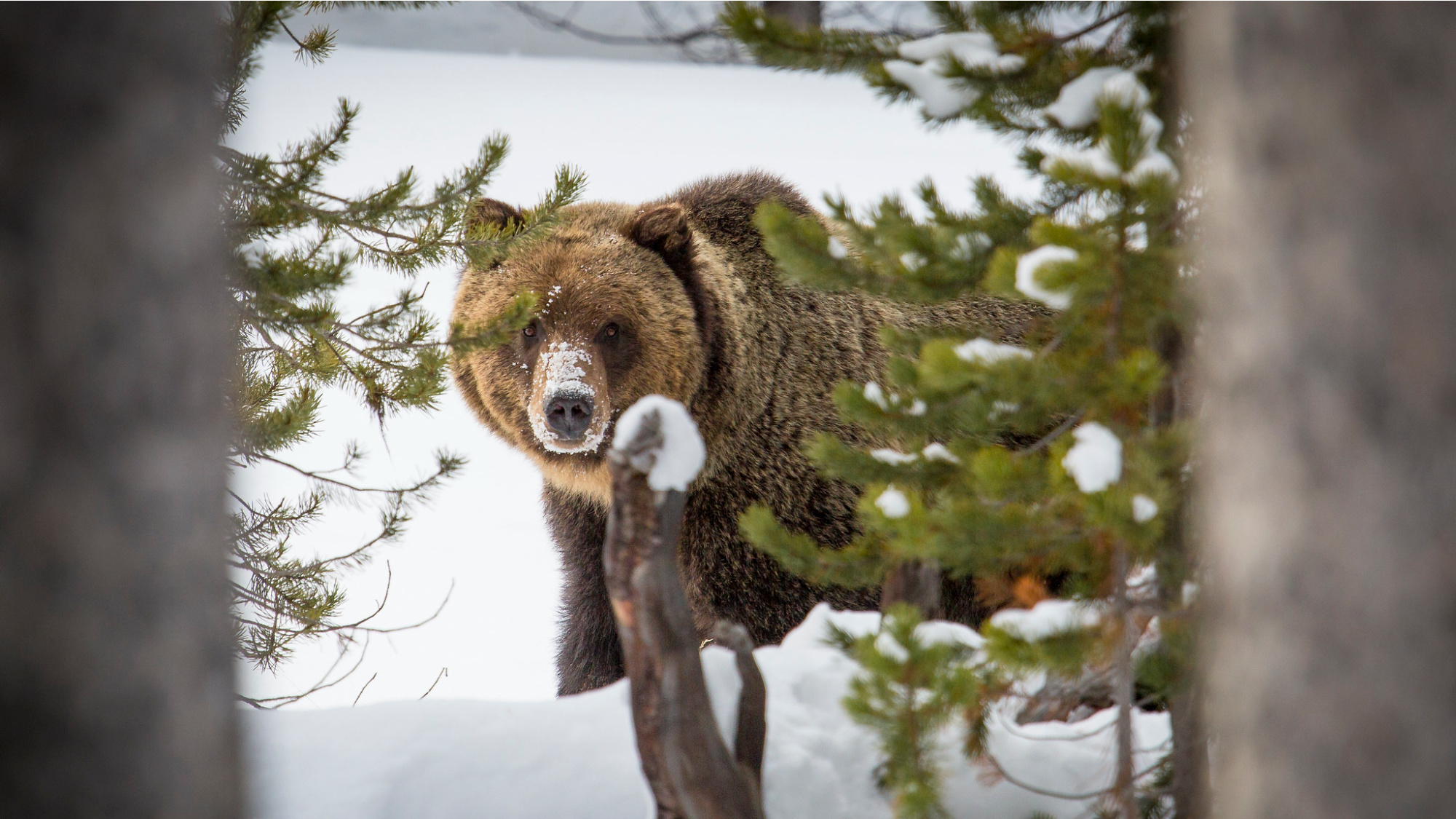

A number of grizzlies have already dispersed into the Bitterroot Mountains from different populations within the Larger Yellowstone and Northern Continental Divide ecosystems. {Photograph} by Neal Herbert / NPS
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service announced on Wednesday a public scoping process and new environmental affect assertion for recovering a breeding inhabitants of threatened grizzly bears within the Bitterroot Mountains of southwestern Montana and jap Idaho. The announcement comes 31 years after the Bitterroot Ecosystem was first recognized as one among six grizzly bear restoration zones within the Decrease 48. It has additionally been 23 years and two months because the USFWS made the ultimate determination to reintroduce the experimental, non-essential inhabitants within the space, a stretch of time that was deemed an unreasonable delay by the U.S. District Courtroom for the District of Montana in March.
Now, the USFWS has till November 2026 to concern a brand new environmental affect assertion and determination on the matter. The company can be accepting public feedback on the plan till March 18.
The Bitterroot ecosystem was first recognized as one among six grizzly bear restoration zones in 1993, as a part of a supplement to the 1982 species recovery plan. In November 2000, the USFWS issued a closing environmental affect assertion and report of determination to reintroduce the bears. However the feds didn’t take any main motion to truly start that reintroduction, shield habitat for the threatened grizzlies that wandered into the realm on their very own, or arrange a citizen’s advisory committee to contain the general public within the course of. On March 15, 2023, U.S. District decide Donald Molloy ruled that the USFWS had not taken proper steps to behave on their November 2000 determination and had unreasonably delayed the restoration, following a lawsuit filed by Alliance of the Rockies towards USFWS grizzly bear restoration coordinator Hilary Cooley.
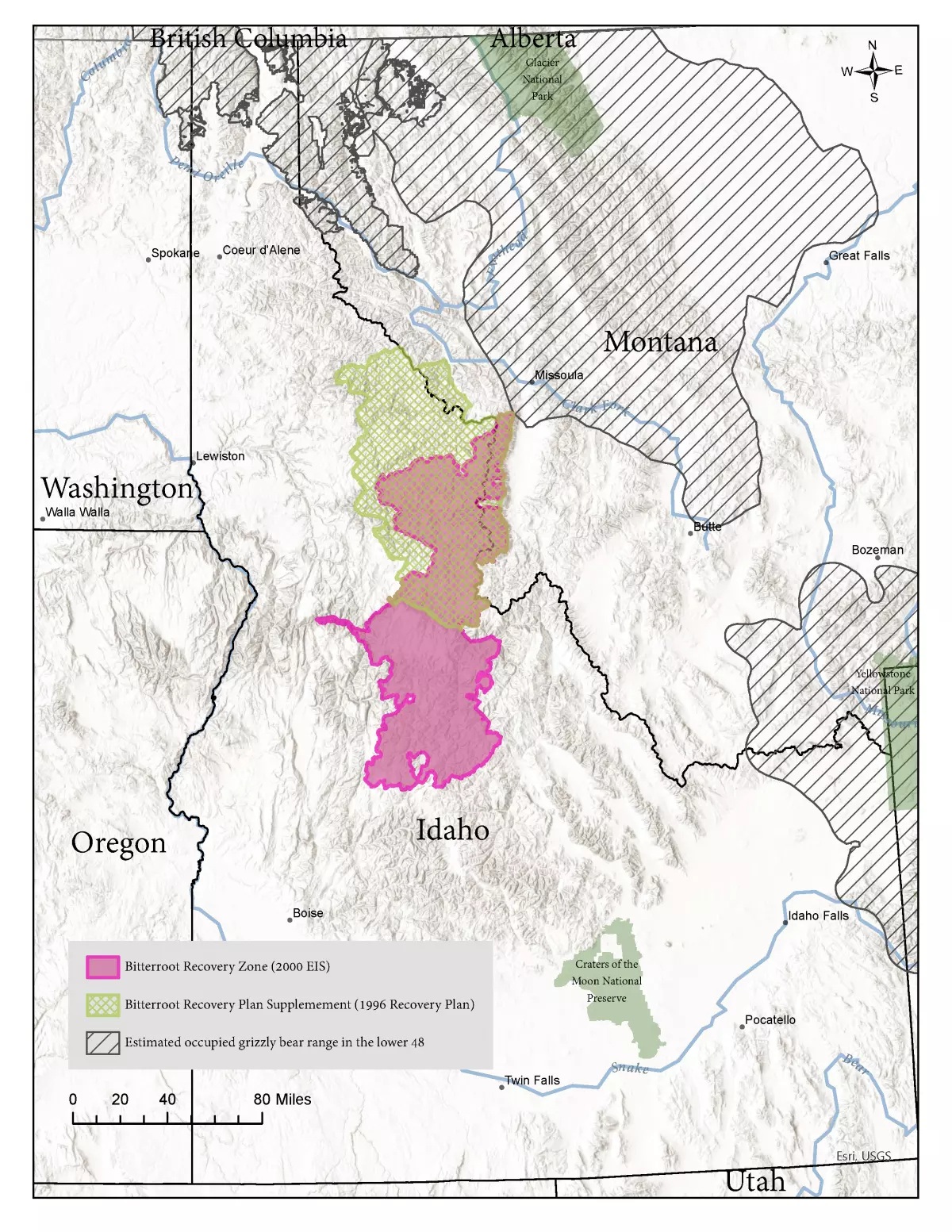
In conversations about grizzly bear restoration within the Decrease 48, the Bitterroot ecosystem has lengthy been accompanied by an asterisk. In different restoration zones just like the Northern Continental Divide and Larger Yellowstone ecosystems, grizzly populations have steadily expanded out of Glacier and Yellowstone nationwide parks and hit sure benchmarks for restoration lately. However the Bitterroot ecosystem has all the time been a spot biologists and wildlife managers hypothesized bears would eventually repopulate on their own. Bears dispersing from the NCDE and GYE are prone to wander into the Bitterroots, primarily based on the proximity of all three areas.
Learn Subsequent: The Clock Is Ticking as the Feds Grapple with Delisting Grizzly Bears
To a sure diploma, they did simply that; reports of grizzlies in the area have popped up lately. However the bears that ranged into the Bitterroot ecosystem have but to attain benchmarks for a breeding inhabitants, which requires two breeding females or one breeding feminine with two consecutive litters, in keeping with the USFWS. Now the feds’ solely possibility is to attempt placing one there, contemplating the mandate ensuing from final 12 months’s lawsuit.
The USFWS is asking for public comment on the scenario for the following 60 days, till March 18. Public conferences with digital entry will happen on Feb. 5 at 6 p.m. MST, Feb. 13 at 6 p.m. MST, and Feb. 14 at 2 p.m. MST.
