When chilly and flu season arrives, it’s often not a query of if you’re going to get sick, however when. The identical holds true for deer. Even the healthiest deer reside arduous lives, and sure circumstances — like meals shortage, brutal winter climate, drought, overpopulation, and so on. — could make deer susceptible to sickness, parasites, and damage. That’s why deer illness is a significant matter of dialogue and examine for wildlife consultants, and the checklist of circumstances, signs, and their penalties is in depth. So we caught up with a wildlife biologist and a wildlife illness ecologist to get the low-down on a few of the commonest deer ailments you may encounter, and what it’s essential to find out about htem.
The Most Widespread Deer Ailments
These 9 deer ailments and circumstances are a few of the largest causes for concern amongst wildlife illness consultants right now. They fall into 4 broad classes primarily based on what causes them: micro organism, viruses, parasites, or prions. We didn’t embody any genetic problems that trigger well being problems like piebaldism, nor will we point out minor parasites that aren’t an actual danger to deer, like nasal botfly larvae. With these guidelines in thoughts, we’ll cowl:
- Arterial worm
- Mind abscess
- Brainworm
- Bovine tuberculosis
- Continual losing illness
- Dermatophilosis
- Big liver flukes
- Hemorrhagic illness (EHD and blue tongue)
- Papillomas
Are Deer Ailments Treatable?
Remedies don’t exist for many of those deer ailments, and the drugs that do enhance signs are largely supposed for livestock or pets. And by the point most sick deer attain the Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, says wildlife illness ecologist and director of the lab Dr. Krysten Schuler, they’re already lifeless.
“We do wish to take a look at these [conditions], but it surely needs to be inside purpose,” says Schuler, whose job is to diagnose deer illness and assist the New York State Division of Environmental Conservation of their wildlife administration efforts. “And there’s not all the time final result for the animal. There are good wildlife hospitals and rehabilitators, however by the point the animals get to us, that’s actually the tip stage.”
Learn Subsequent: The Best Skinning Knives
Companies handle entire herds and populations for illness resilience and total well being and well-being, Schuler says, which improves every particular person deer’s probabilities of avoiding and surviving illness outbreaks. Hunters additionally play an important function by observing and reporting sick deer to their state businesses.
“It’s extremely essential for the general public to report sick and dying animals,” says Matt Ross, wildlife biologist and director of conservation for the National Deer Association. “Lots of people might not do this, however we’d like you to report that stuff as a result of that’s how we get a greater sense of what’s happening.”
By that, Ross signifies that whereas it could be too late to avoid wasting that particular person deer, realizing what sickened or killed it might probably assist officers monitor and handle outbreaks and study extra about rarer deer ailments. This intel will help inform the general public about what’s taking place with their deer herds.
Bacterial Infections in Deer
A deer’s conceal is roofed in naturally-occurring, residing micro organism. That bacterial presence is regular and wholesome. Hassle arises when that micro organism enters a wound, when dangerous micro organism is launched to a deer’s system, or when the great micro organism will get out of steadiness (which regularly causes pores and skin issues). Bacterial infections in people, pets, and livestock are sometimes handled with antibiotics, however that’s an possibility for wild deer for apparent causes.
Bovine Tuberculosis
Presently, bovine tuberculosis solely exists in wild deer herds within the Higher Midwest. However as a result of it might probably move to people, it’s price mentioning right here. Most instances of bovine tuberculosis in people come from consumption of unpasteurized dairy merchandise, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
What’s bovine tuberculosis?
The identical micro organism that causes tuberculosis in cattle and captive cervids, Mycobacterium bovis, can infect free-roaming whitetail deer by respiratory transmission, the identical approach you catch a chilly when a buddy coughs on you. An early-stage tuberculosis-infected deer might need pus-filled abscesses and lesions on the partitions of its chest cavity and lungs, that are solely seen when you’ve subject dressed the deer. Lesions may also seem on the deer’s lymph nodes.
Signs of bovine tuberculosis in deer
Respiratory sickness, coughing, nasal discharge, wheezing, fatigue, hassle respiration, emaciation, lethargy, and lesions in chest cavity and/or on lymph nodes. Bovine tuberculosis is usually deadly for deer.
Can I eat meat from a deer with bovine tuberculosis?
Whereas the illness passes by respiratory transmission, it might probably additionally move by contact with an open wound. That’s why hunters usually tend to contract bovine tuberculosis from wild deer than nonhunters. Carrying gloves whereas subject dressing deer is an effective approach to stop catching bovine tuberculosis.
Mind Abscess

A mind abscess happens when a head wound turns into severely contaminated and places stress on the mind. Bucks typically maintain head accidents whereas combating throughout the rut, and are due to this fact extra more likely to contract this deer illness.
What’s mind abscess?
A pressure of naturally-occurring pores and skin micro organism referred to as Trueperella pyogenes enters a flesh wound on a buck’s head. It eats by the cranium into the mind case, the place it grows. Fairly quickly, a big, pus-filled abscess takes up some portion of the buck’s cranium.
Signs of mind abscess in deer
A deer with a mind abscess might have a visual wound on its head, swollen eyes, swollen joints, or foot sores. A deer with a damaged pedicle or gap within the head could also be in danger for a mind abscess. Often head trauma is adopted by fever, lethargy, and poor coordination. A mind abscess is all the time deadly.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with mind abscess?
No. This sort of bacterial an infection can unfold within the deer’s bloodstream and due to this fact hunters shouldn’t knowingly eat meat from a buck with mind abscess.
Dermatophilosis
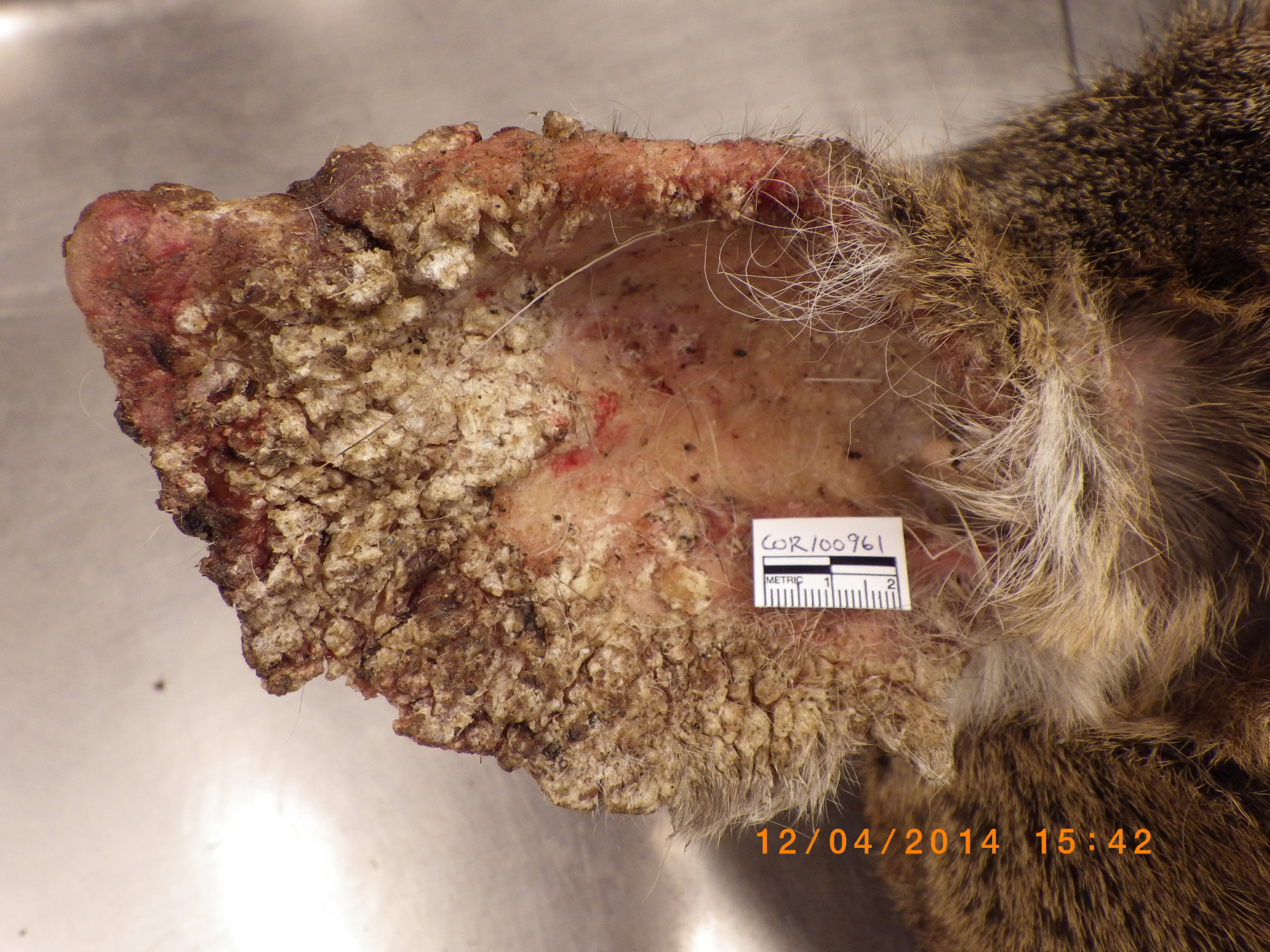
Also called “rain rot,” this crusty pores and skin situation may have an effect on different cervids like elk and moose, in addition to livestock.
What’s dermatophilosis?
A novel bacterium referred to as Dermatophilus congolensis, which behaves extra like a fungus than micro organism, proliferates on the pores and skin in moist, heat, and soiled circumstances. That overabundance of micro organism wreaks havoc on the host deer’s conceal.
Signs of dermatophilosis in deer
Lesions, hair loss, pustules, and sores. Dermatophilosis in deer is commonly mistaken for mange. Dermatophilosis appears gross, but it surely’s hardly ever deadly for deer.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with dermatophilosis?
Whereas this an infection doesn’t have an effect on a deer’s muscle mass, it might probably move to people simply and trigger lesions and sores on any pores and skin that touches the deer. Take into account avoiding a deer with dermatophilosis altogether, or sporting gloves if in case you have no alternative however to the touch one.
Viruses in Deer
Viruses are nonliving microbes that may trigger every part from large pores and skin warts to loss of life in deer. Not like residing micro organism, which may be killed with antibiotics, viruses don’t have cures and contaminated deer typically die from them.
Hemorrhagic Ailments
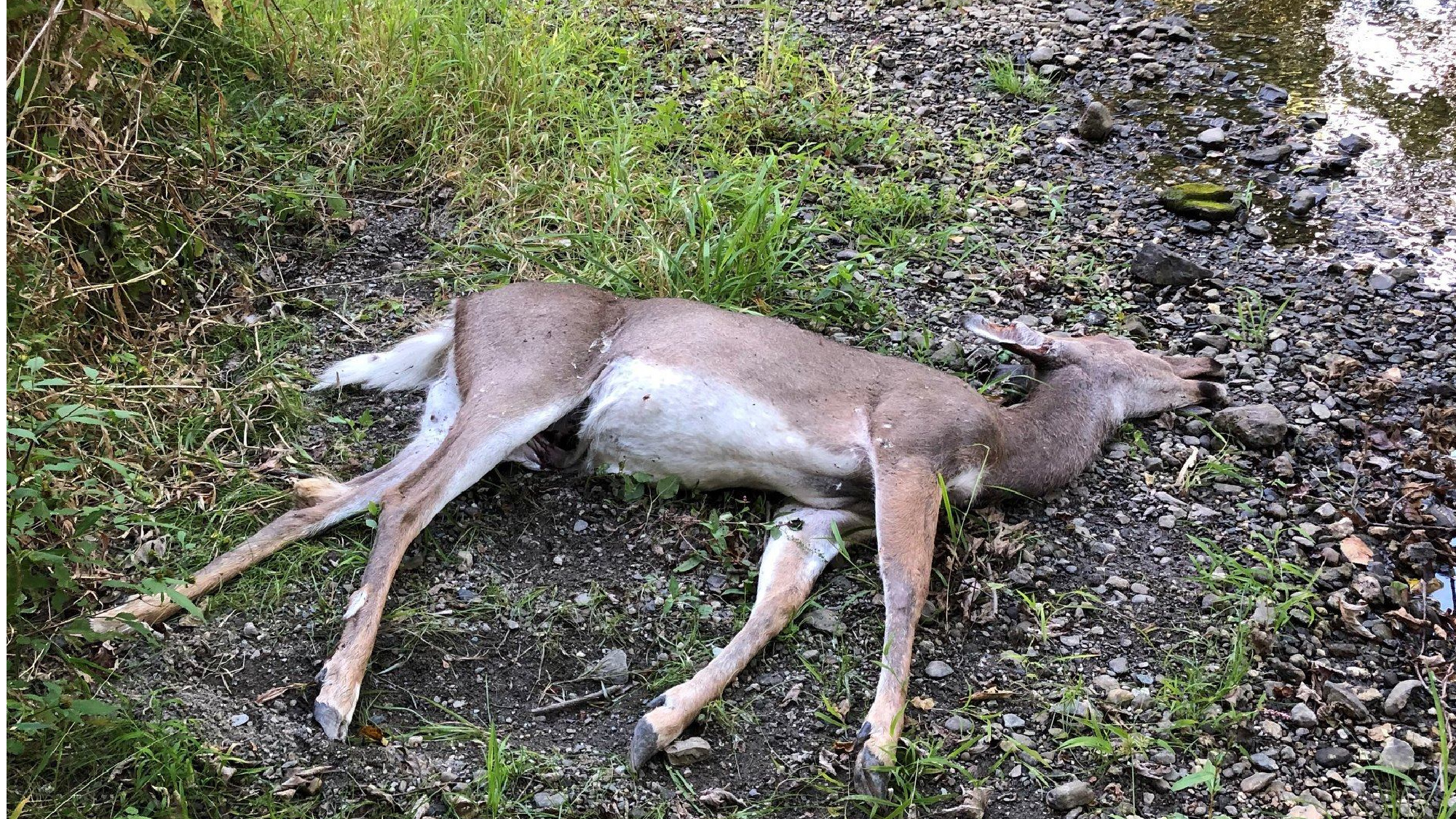

The 2 main hemorrhagic ailments that deer can contract, epizootic hemorrhagic illness and blue tongue, are very carefully associated and trigger related signs. The one difference between the two is the particular virus that causes them. Normally, deer catch EHD whereas livestock catch blue tongue, however deer may contract blue tongue in uncommon situations. Be looking out for these viruses throughout the heat summer time months when biting bugs are particularly prevalent. In the event you discover a lifeless deer close to water, there’s probability it died from EHD; the fever related to the illness pushes the deer towards water sources, Schuler says.
What’s EHD?
Small, biting midges move this viral illness to deer. Deer can’t transmit it to one another, however that doesn’t cease it from being arguably the deadliest deer illness in North America. EHD is very problematic within the Southeast, Midwest, and the Nice Plains. Deer with EHD often die inside two weeks of an infection.
Signs of EHD in deer
Fatigue, poor coordination, and bruising and extreme swelling within the mouth, head, neck, and tongue. Signs seem inside 2 to 10 days of an infection, and deer often die inside two days of experiencing signs. On uncommon events, deer will survive EHD. Search for cracked hooves as an indication that they lived by this deer illness.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with EHD?
Consuming the meat from a deer that’s visibly unwell with EHD will not be really useful. Testing for the illness after harvesting the deer isn’t crucial, since signs are virtually all the time instantly seen in an contaminated deer.
Papillomas
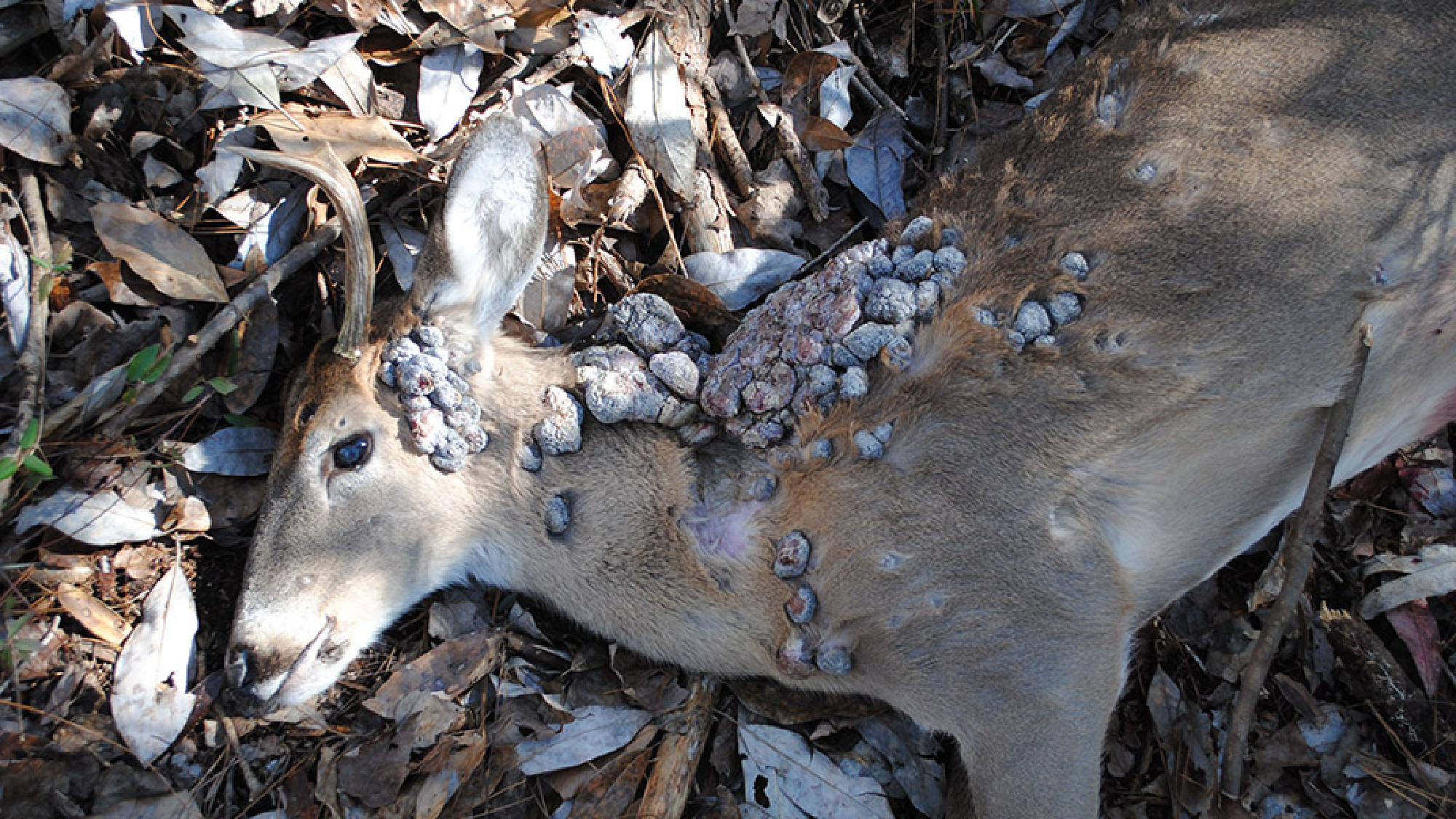

In any other case referred to as “cutaneous fibromas,” these massive, unpleasant deer warts may gross you out. Whereas they could appear to be an indication of some grotesque inside illness, they’re truly fairly innocent.
What are papillomas?
Papillomas are brought on by a virus and may be unfold round a deer’s physique in the event that they lick one affected space after which lick an unaffected space. They’ll develop to the scale of huge grapefruits and can even generally fall off, however they don’t often affect the deer’s total well being. In uncommon instances the warts can develop so massive that they impede the deer’s airways or impede its motion.
Signs of papillomas in deer
Warts ranging in dimension from an engorged tick to a big grapefruit wherever on the physique. Until they trigger respiration or motion issues, papillomas are hardly ever deadly for deer.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with papillomas?
Sure, meat from a deer with papillomas is unquestionably nonetheless suitable for eating. Take into account sporting gloves and taking additional precautions when subject dressing and skinning the deer.
Parasites in Deer
Parasites reside, multi-celled organisms that survive by feeding on (and infrequently residing inside) a number animal. From hair-thin worms to large grubs, deer reside with a wide range of parasites which may make your pores and skin crawl. Fortunately, most of them are fairly innocent.
Arterial Worm
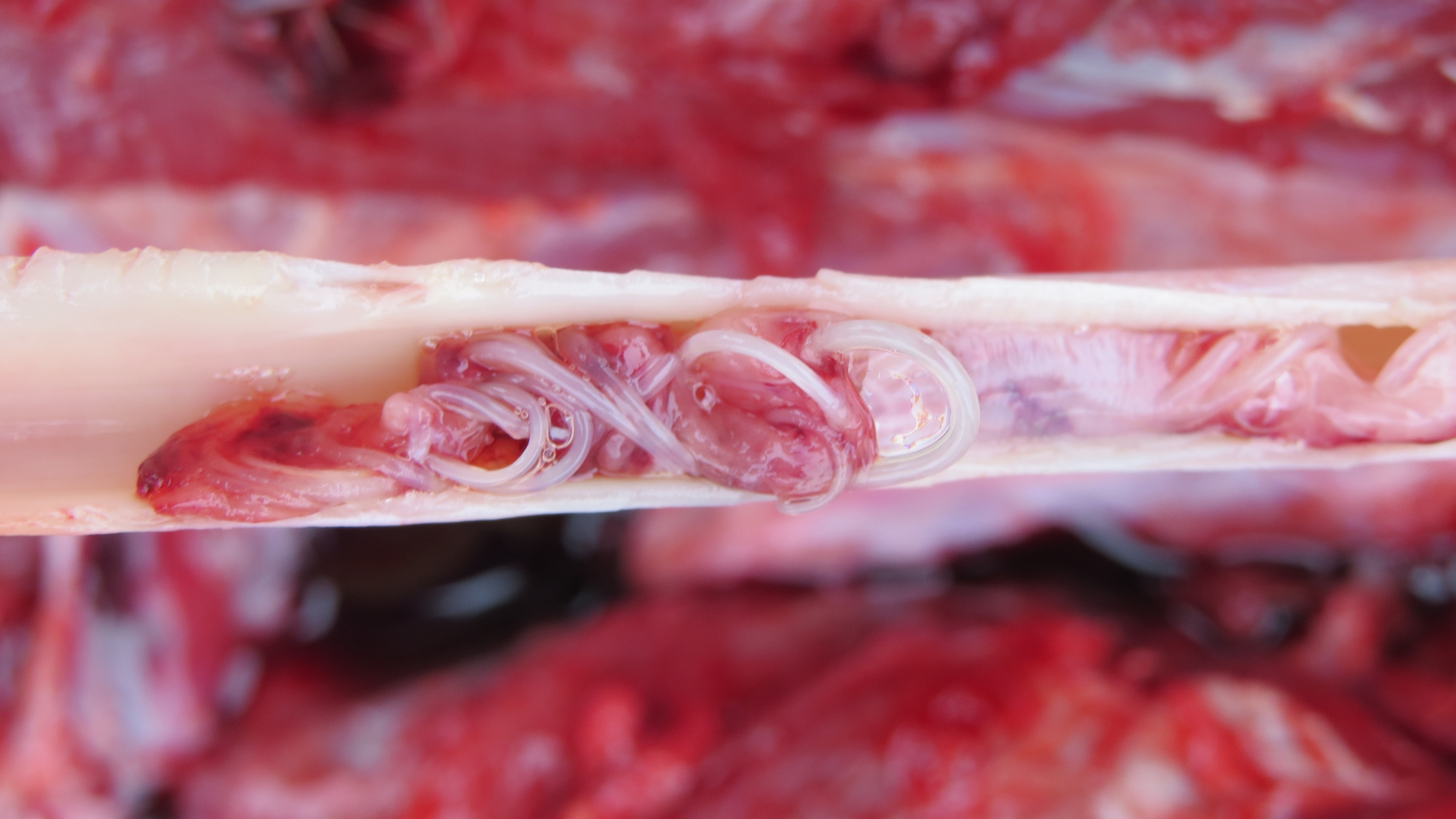
In the event you’ve ever seen a deer with a big lump of unswallowed meals caught in its cheek, it most likely had arterial worm.
What’s arterial worm?
When a number fly bites a deer, roundworm larvae journey from the mouthparts of the fly right into a deer’s bloodstream. These larvae ultimately find yourself within the deer’s carotid artery, which runs alongside its neck. If the worms develop large enough, they’ll impede blood movement to the deer’s jaw, impeding the deer’s potential to chew and swallow correctly. This can lead to a ball of impacted meals, virtually like a lip filled with chewing tobacco, caught within the deer’s mouth and inflicting problems.
Signs of arterial worm in deer
A golfball- to grapefruit-sized lump in a deer’s mouth is a traditional signal of arterial worm. If the impaction is dangerous sufficient, it may trigger a secondary an infection, however that is unlikely. Arterial worm isn’t deadly to deer except it causes an infection or leads to a whole lack of ability to devour meals.
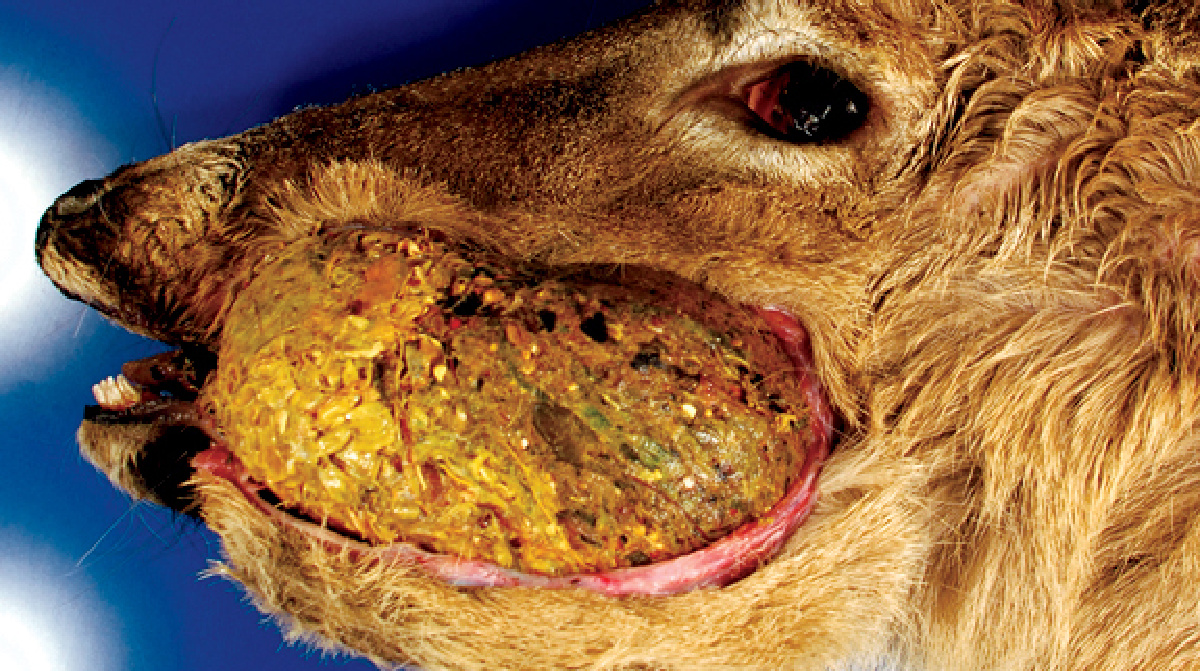
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with arterial worm?
Sure if the meals impaction is minor. But when the deer is exhibiting indicators of secondary an infection from numerous impacted meals, akin to a bloody, pus-filled wound or ruptured pores and skin across the mouth, keep away from consuming the meat, says the NDA.
Brainworm
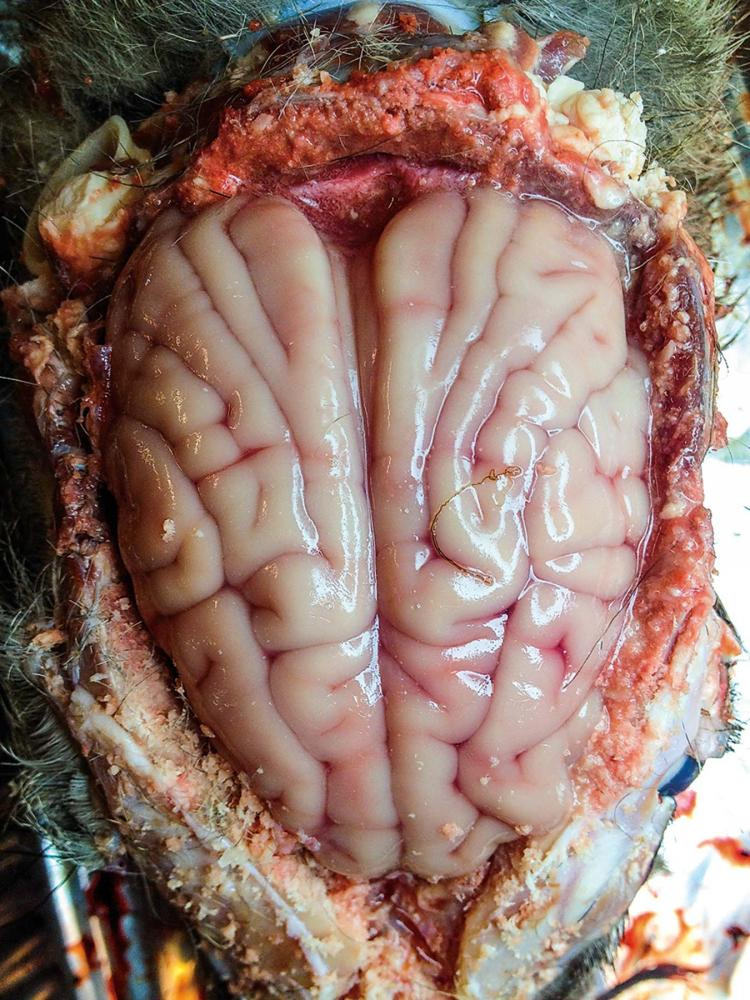
Whereas this parasite appears like a mind-controlling loss of life sentence, the variety of deer that truly have problems resulting from brainworm is surprisingly low — lower than 1 %, in keeping with Schuler.
What’s brainworm?
A brainworm is a worm as skinny as a human hair that swims round within the meninges, or outer mind case, of deer. It doesn’t often have an effect on deer.
Signs of brainworm in deer
Brainworm in deer is often undetectable, except eggs are deposited within the choroid plexus, or a community of blood cells and cells within the fluid-filled components of the mind, which might trigger mind swelling. Brainworm is nearly by no means deadly to deer.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with brainworm?
Sure. Moreover, it’s unlikely you’ll even be capable of discover in case your deer had brainworm.
Big Liver Flukes
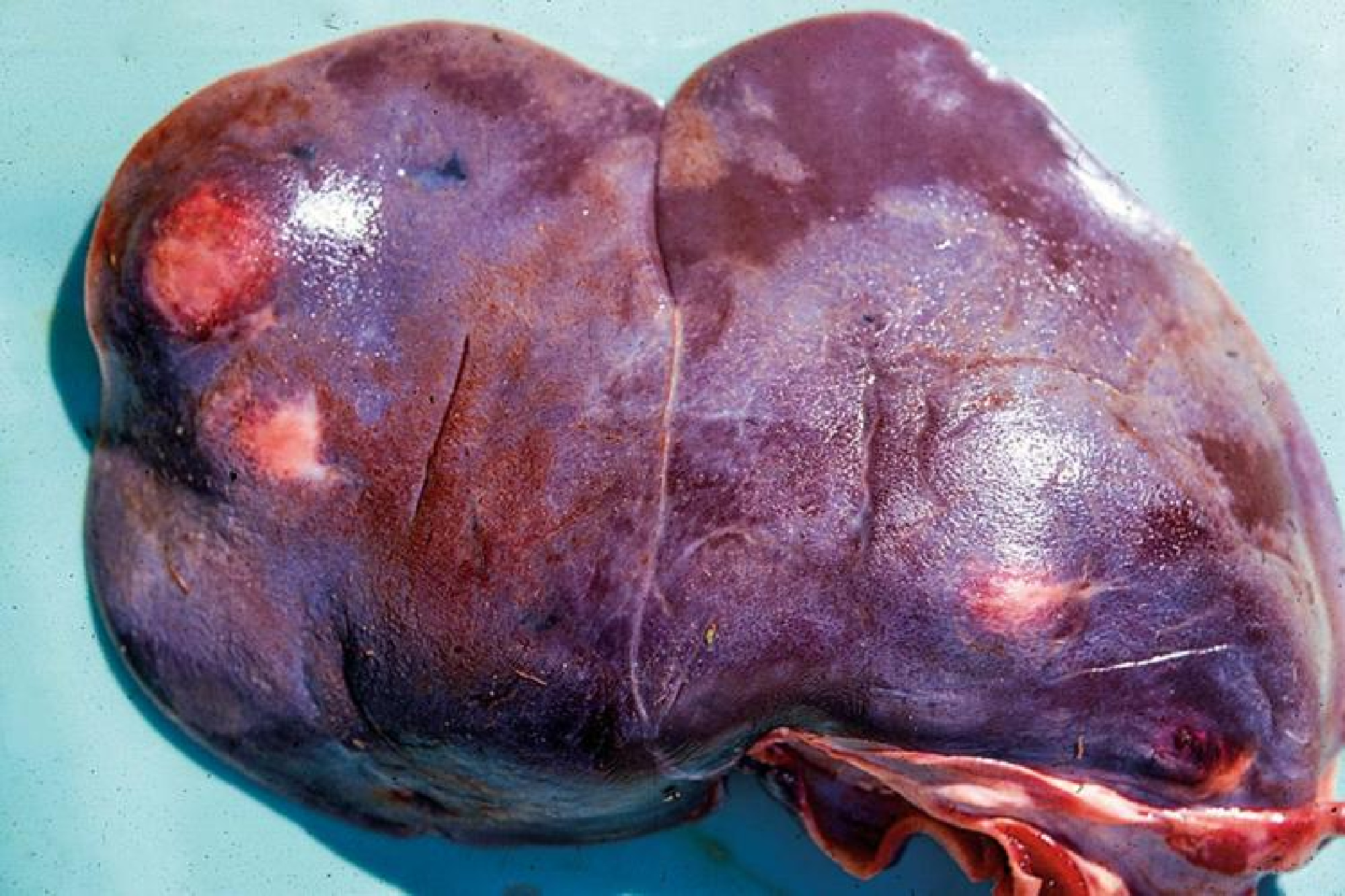
The identify appears like a villain from a nasty superhero flick, however this parasite is much extra widespread than hunters may notice.
What are large liver flukes?
Big liver flukes enter a deer’s digestive system as late-stage larvae residing within the deer’s meals sources. The flukes journey to the deer’s liver and full their life cycle there, laying eggs that exit again into the world by the deer’s feces. The flukes hatch on the bottom and migrate to their main host, mud snails, the place they rework into the larvae, beginning the cycle over once more.
Signs of large liver flukes in deer
No exterior signs, however a hunter may encounter massive white or brown lesions or holes contained in the deer’s liver paying homage to Swiss cheese. A few of these holes may have liver flukes residing inside them. The flukes are often crimson or tan-brown, oval-shaped and flat, and may be as much as 3 inches lengthy. Big liver flukes are hardly ever deadly to deer.
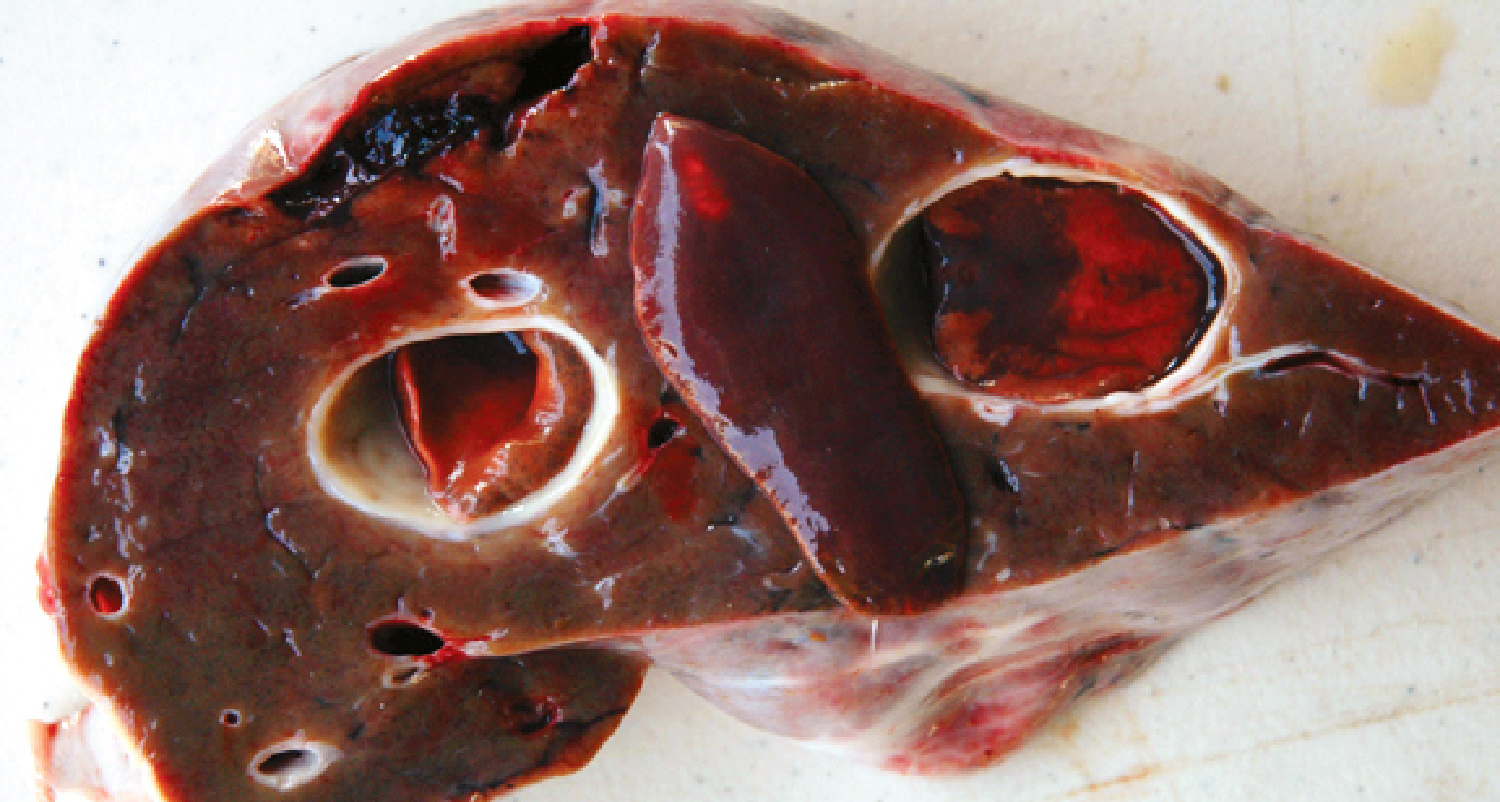
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with large liver flukes?
If you may get previous the ick issue, sure. Venison is unhurt by the presence of large liver flukes so long as secondary an infection in different components of the deer’s physique hasn’t occurred. Simply don’t devour a fluke-infected liver.
Prion Ailments in Deer
There’s just one deer illness identified to be brought on by prions, but it surely’s iconic sufficient to get its personal class. Mad cow illness and sheep scrapie are two different examples of prion ailments in animals which may sound acquainted.
Continual Losing Illness

In the event you haven’t heard of this deer illness by now, it’s about time you probably did. And no, it’s not truly a zombie deer disease.
What’s persistent losing illness?
Misfolded proteins referred to as prions basically burn holes within the deer’s mind and trigger extreme bodily decline earlier than killing the deer slowly. Prions are extremely contagious, particularly as a result of they’ll survive on licking branches and in soils for years, and it takes temperatures of over 900 levels Fahrenheit to destroy them.
Signs of persistent losing illness in deer
Deer with persistent losing illness are symptomatic for first 12 months or two earlier than exhibiting lethargy, weight reduction, drooling, poor coordination, and desensitization to close by threats like individuals, predators, and vehicles. Continual losing illness is all the time deadly to deer.
Can I nonetheless eat the meat from a deer with persistent losing illness?
You possibly can, however you shouldn’t. There is no such thing as a identified case of a human contracting CWD by consuming venison from an contaminated deer. Even so, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advise disposing of the meat from a CWD-positive deer, as do wildlife biologists, state businesses, and conservation teams.
Deer Illness FAQ
The phrase “zombie deer disease” refers to persistent losing illness, but it surely’s an inaccurate nickname for CWD that does extra hurt than good. The identify is assumed to originate from how CWD-causing prions burn holes within the deer’s mind, but it surely additionally makes it sound like CWD-infected deer are stumbling round and aggressively biting different deer, which isn’t the case.
No, deer don’t get Lyme illness, regardless of what number of ticks chunk them yearly. That’s as a result of their blood kills Lyme-disease-causing bacteria, permitting them to coexist with ticks in relative peace.
The reply adjustments relying on the area. Continual losing illness is extraordinarily prevalent in components of Wyoming and Wisconsin, for instance. Hemorrhagic ailments change into fairly widespread and prevalent within the Southeast throughout sure instances of 12 months.
Up to now, most main deer ailments don’t present any indicators of leaping from deer to people. CWD, for instance, has but to cross over to human populations. However that doesn’t imply that it couldn’t occur sometime, and wildlife illness pathologists and different consultants within the subject are working arduous to raised perceive these odds.
Last Ideas on Deer Illness
Deer, like all wildlife species, reside a life that’s closely uncovered to micro organism, viruses, parasites, prions, and different naturally-occurring sources of deer illness. This shouldn’t come as a shock — or be trigger for concern.
“Deer reside laboratories,” Ross says. “They’re a part of an ecosystem, similar to us people are. And the presence of those ailments shouldn’t be trigger for alarm. However presence in massive numbers the place they’re having a detrimental inhabitants affect is the place you must get nervous. So anticipate these deer ailments to be on the market. Nevertheless it’s only a matter of understanding and figuring out them, and reporting them.”
